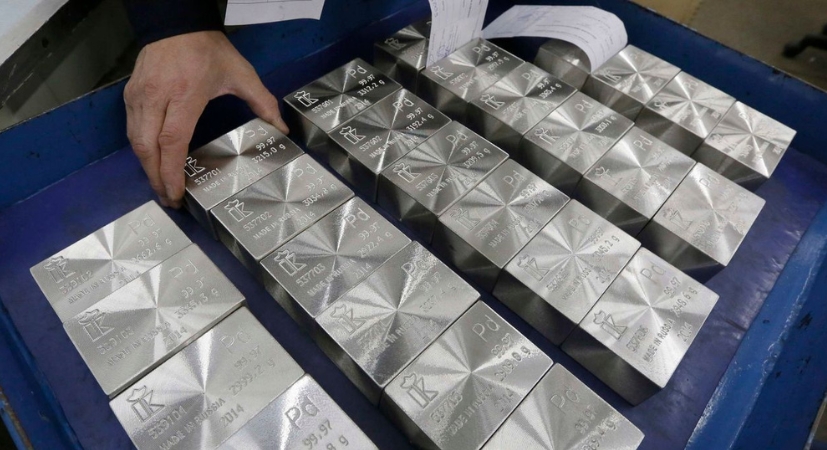
Atlas Ore stands as a pioneer in the palladium mining industry, renowned for its utilization of cutting-edge technologies and commitment to sustainable practices. With a steadfast dedication to operational excellence and environmental stewardship, Atlas Ore's palladium mining operations are characterized by safety, innovation, and community engagement.
Palladium holds significant importance in various industries, particularly in automotive manufacturing, electronics, and catalytic converters. As a primary supplier of palladium, Atlas Ore meets the escalating demand for this precious metal by harnessing its expertise and resources to extract and process palladium ore with precision and efficiency.
Uses
Palladium, a rare and valuable metal, finds application across various industries due to its unique properties. Here are some common uses of palladium:
- Electronics: Palladium is used in the manufacturing of multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), a vital component in electronic devices such as smartphones, computers, and automotive electronics. Palladium is also used in connectors, switches, and sensors due to its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Jewelry: Palladium is prized for its rarity, durability, and lustrous appearance, making it a popular choice for crafting high-quality jewelry. Palladium jewelry is hypoallergenic, tarnish-resistant, and lighter than gold, making it an attractive option for wedding bands, engagement rings, and fine jewelry pieces.
- Dental Materials: Palladium is used in dental alloys for crowns, bridges, and dentures due to its biocompatibility, strength, and resistance to corrosion. Palladium-based dental materials offer superior aesthetics, durability, and compatibility with oral tissues.
- Hydrogen Storage: Palladium is used in hydrogen storage technologies, such as palladium membranes and palladium-based alloys, for storing and releasing hydrogen gas in fuel cells, hydrogen purification systems, and hydrogen sensors. Palladium's ability to absorb large volumes of hydrogen at room temperature makes it an efficient and compact storage medium for hydrogen fuel.
- Chemical Catalysts: Palladium catalysts are widely used in chemical synthesis, organic reactions, and petroleum refining processes. Palladium-catalyzed reactions, such as cross-coupling reactions and hydrogenation reactions, play a crucial role in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemical industries.
- Watchmaking: Palladium is used in luxury watchmaking for cases, dials, and clasps due to its scratch resistance, lightweight, and hypoallergenic properties. Palladium watches are highly valued for their elegance, durability, and exclusivity.
- Water Treatment: Palladium-based catalysts are employed in water treatment technologies for removing contaminants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), from drinking water and industrial wastewater. Palladium catalysts facilitate oxidation and degradation of organic pollutants, ensuring clean and safe water supply.
- Renewable Energy: Palladium is used in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) as a catalyst for the electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. PEMFCs are a promising technology for powering electric vehicles, portable electronics, and stationary power systems with clean and efficient energy.
- Artificial Hip Joints: Palladium-based alloys are used in orthopedic implants, such as artificial hip joints and knee replacements, due to their biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Palladium implants offer long-term durability and compatibility with the human body, improving patient mobility and quality of life.
These are just a few examples of the diverse range of applications for palladium across industries. Its versatility, durability, and unique chemical properties make it a valuable metal in modern technology, healthcare, and environmental protection.
Like a rare bloom in a field of ordinary, platinum stands out as a symbol of rare beauty and unmatched quality.Unknown