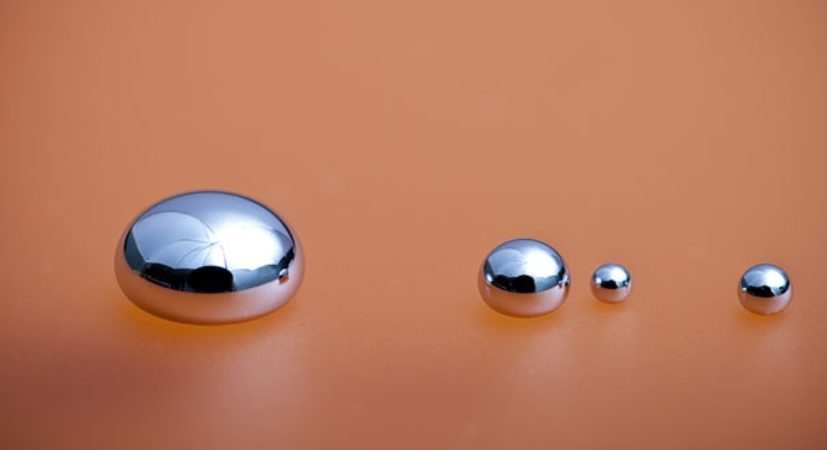
As an environmentally conscious and safety-focused company, Atlas Ore approaches mercury mining with a commitment to responsible practices and sustainable operations. With a wealth of experience and expertise in the mining industry, Atlas Ore employs cutting-edge technologies and stringent safety protocols to ensure the well-being of its workforce and the surrounding environment.
Mercury mining, while essential for various industrial processes, presents unique challenges due to the toxic nature of mercury and the potential environmental impact associated with its extraction and processing. Atlas Ore recognizes these challenges and prioritizes safety and environmental stewardship in all aspects of its mercury mining operations.
Uses
Mercury, despite its hazardous nature, finds application in various industries due to its unique properties. Here are some common uses of mercury:
- Dental Fillings: Mercury is used in dental amalgam, a mixture of mercury and other metals such as silver, tin, and copper, for dental fillings due to its durability and ease of use. However, its use has decreased due to health and environmental concerns.
- Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining: Mercury is used in artisanal and small-scale gold mining to extract gold from ore by forming a gold-mercury amalgam. This method, known as amalgamation, poses significant environmental and health risks due to mercury pollution.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Mercury compounds are used in various chemical processes, including the production of chlorine and caustic soda, as catalysts in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of fluorescent lights, batteries, and electrical equipment.
- Medical Instruments: Mercury is used in certain medical instruments, such as blood pressure monitors and sphygmomanometers, for measuring blood pressure. However, its use in healthcare settings has been decreasing due to safety concerns.
- Laboratory Equipment: Mercury is used in certain laboratory equipment, such as mercury vapor analyzers and mercury electrodes, for measuring trace amounts of mercury and conducting electrochemical experiments.
- Anti-fouling Paints: Mercury-based compounds, such as mercuric chloride and phenylmercuric acetate, have been used in anti-fouling paints to prevent the growth of marine organisms on ship hulls and underwater structures. However, their use has been phased out due to environmental concerns.
These are some of the common uses of mercury across industries, although many of these applications have decreased or been phased out due to environmental and health concerns associated with mercury exposure.
Mercury, the mysterious metal, whispering secrets of the ancient alchemists, yet bearing the weight of modern science on its liquid shoulders.Unknown