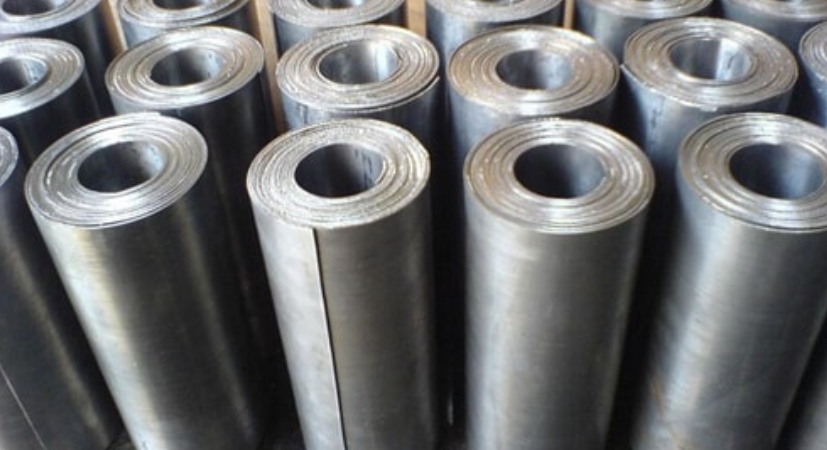
Atlas Ore, a leader in the mining industry, stands at the forefront of lead mining operations with a focus on innovation, sustainability, and responsible resource management. Leveraging cutting-edge technologies and a wealth of expertise, Atlas Ore's lead mining endeavors are characterized by efficiency, safety, and environmental stewardship.
At the heart of Atlas Ore's lead mining operations lies a commitment to operational excellence and adherence to the highest safety standards. The company employs state-of-the-art equipment and stringent safety protocols to ensure the well-being of its workforce and the surrounding communities. From comprehensive training programs to advanced safety monitoring systems, Atlas Ore prioritizes safety at every stage of the mining process.
Uses
Lead, a versatile and valuable metal, finds application across various industries due to its unique properties. Some common uses of lead include:
- Batteries: Lead-acid batteries are one of the primary uses of lead, particularly in automotive and industrial applications. These batteries are used in vehicles, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup power systems due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
- Construction: Lead is used in construction materials, such as roofing materials, flashing, and waterproofing membranes. Its malleability and corrosion resistance make it a preferred choice for sealing joints and protecting structures from water damage.
- Ammunition: Lead is a key component in ammunition manufacturing, where it is used to produce bullets and shot for firearms. Its density and ability to deform upon impact make it ideal for creating projectiles with desired ballistic properties.
- Weights and Counterweights: Lead's high density makes it useful for producing weights and counterweights in various applications, including balancing mechanisms in machinery, vehicle wheel balancing, and diving weights for scuba diving.
- Radiation Shielding: Due to its high density and ability to absorb radiation, lead is commonly used in radiation shielding applications. It is used in medical facilities for shielding X-ray rooms, nuclear medicine facilities, and radiation therapy equipment to protect patients and healthcare workers from radiation exposure.
- Cable Sheathing: Lead is used as a sheathing material for electrical cables, providing protection against moisture, corrosion, and electromagnetic interference. Lead-sheathed cables are commonly used in underground and underwater applications where durability and reliability are essential.
- Pigments: Lead-based pigments, such as lead carbonate (white lead) and lead chromate (yellow lead), have been historically used in paints, coatings, and ceramics for their brightness, opacity, and durability. However, due to health and environmental concerns, their use has been significantly reduced in many countries.
- Fishing Equipment: Lead is used in fishing tackle, including sinkers, jigs, and lures, to provide weight for casting and to help anglers target specific depths in water bodies.
- Soundproofing: Lead sheets or barriers are used for soundproofing applications in buildings, studios, and industrial settings to reduce noise transmission and improve acoustics.
- Nuclear Industry: Lead is used as a radiation shielding material in nuclear reactors, nuclear waste containers, and other nuclear facilities to protect personnel and the environment from radiation exposure.
These are just a few examples of the diverse range of applications for lead across industries. Despite its versatility, it's essential to handle and dispose of lead-containing products responsibly to minimize health and environmental risks.
Lead, like a true artist, doesn't know what it is until it's tested.Jason Mraz